Academic Article
3D LiDAR modeling with iPhone Pro in an archaeo-spelaeologic context. Results and prospects
- Title
- 3D LiDAR modeling with iPhone Pro in an archaeo-spelaeologic context. Results and prospects
- Date
- 2024
- Is Part Of
-
 Archeologia e Calcolatori
Archeologia e Calcolatori
- Volume
- 35
- Issue
- 2
- Pages
- 421-430
- Language
- eng
- Rights
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
- Abstract
- For some years now, both in the archaeological and speleological fields, experiments have been carried out with portable MLS (Mobile Laser Scanner) or HMLS (Hand-held Mobile Laser Scanner) scanners that use LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology. This choice is due to their basic characteristics such as ease of use, reliability, efficiency and (a fact not to be underestimated) low costs compared to traditional indirect survey systems. These characteristics have made these tools extremely popular, especially since this technology can be used by owners of Apple devices, which has made it available for its tablets and smartphones, thanks to the ever-increasing sensor miniaturization. On the basis of some encouraging data presented in an archaeometry paper (Fiorini 2022) and from direct experiences in various underground sites proposed by several Italian caving groups, the authors have decided to test the device performance in the context of exploration and research on artificial cavities in the archaeological field which, very often, due to size and constraints, do not allow the use of other devices. Through the presentation of some case studies, it was possible to show the advantages and the limitations in the use of this technique in the archaeo-spelaeological field.
- Zotero References Collection
- https://www.zotero.org/groups/5293298/bidiar/collections/3KC77372
- Cites
- Scansioni dinamiche in archeologia dell’architettura: test e valutazioni metriche del sensore LiDAR di Apple
- Evaluation of the Apple iPhone 12 Pro LiDAR for an Application in Geosciences
- Apple iPad Pro: test e valutazioni metriche sul sensore LiDAR integrato
- L'acquedotto romano della Campania "Fontis Augustei Aquaeductus"
- Comparative analysis of different techniques for the topographic survey of artificial galleries: The case study of the INGV Messina headquarter geophysical tunnel (Sicily, Italy)
- Studi e ricerche sull'anfiteatro Flavio puteolano
- The Aqua Augusta. Regional water supply in Roman and late antique Campania: An historical and archaeometrical study
- Aqua Augusta, nuove evidenze dai Campi Flegrei
- The Pozzuoli (Naples, Italy) Flavian amphitheatre cisterns: A basic experience in 3D modelling with LiDAR
- Acquedotto Augusteo della Campania Notizie preliminari sul tratto Fuorigrotta - Coroglio (Napoli)
- Aqua augusta campaniae: considerazioni sulle morfologie degli spechi in area flegrea
- The Aqua Augusta and control of water resources in the Bay of Naples
- Pouzzoles antique : histoire et topographie
- Intus in tenebris. Scienza e tecnica nelle opere ipogee romane
- Acquedotto Augusteo della Campania Notizie preliminari sul tratto Fuorigrotta - Coroglio (Napoli)
- Acqua e acquedotti romani: fontis augustei aquaeductus
- I reali scavamenti nell’anfiteatro di Pozzuoli
Export
- Media
-
 The Flavian amphitheater in Pozzuoli (photo G.W. Ferrari)
The Flavian amphitheater in Pozzuoli (photo G.W. Ferrari) -
 Cistern positions in the Flavian amphitheater in Pozzuoli (from Ferrari 2023, fig. 3)
Cistern positions in the Flavian amphitheater in Pozzuoli (from Ferrari 2023, fig. 3) -
 Top view of a two-chambers cistern and a main ambulacrum section in the Flavian amphitheater (Cocceius Association)
Top view of a two-chambers cistern and a main ambulacrum section in the Flavian amphitheater (Cocceius Association) -
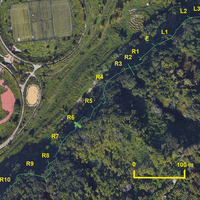 Augustan aqueduct side branch section near the Bagnoli reclamation area, with the identified adits (from De Simone, Ferrari 2024, fig. 4)
Augustan aqueduct side branch section near the Bagnoli reclamation area, with the identified adits (from De Simone, Ferrari 2024, fig. 4) -
 Augustan aqueduct at Bagnoli: 3D model of R9 adit, with a superposed channel section (Cocceius Association)
Augustan aqueduct at Bagnoli: 3D model of R9 adit, with a superposed channel section (Cocceius Association) -
 Augustan aqueduct at Bagnoli: top view of the junction between two digging teams, between adits R7 and R8 (Cocceius Association)
Augustan aqueduct at Bagnoli: top view of the junction between two digging teams, between adits R7 and R8 (Cocceius Association) -
 Scan with an illuminator/power bank support in an underground aqueduct channel (photo G.W. Ferrari)
Scan with an illuminator/power bank support in an underground aqueduct channel (photo G.W. Ferrari)
Position: 4213 (5 views)

